Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Vein Specialists of the Carolinas
“All We Do Is Veins, All Day Every Day.”
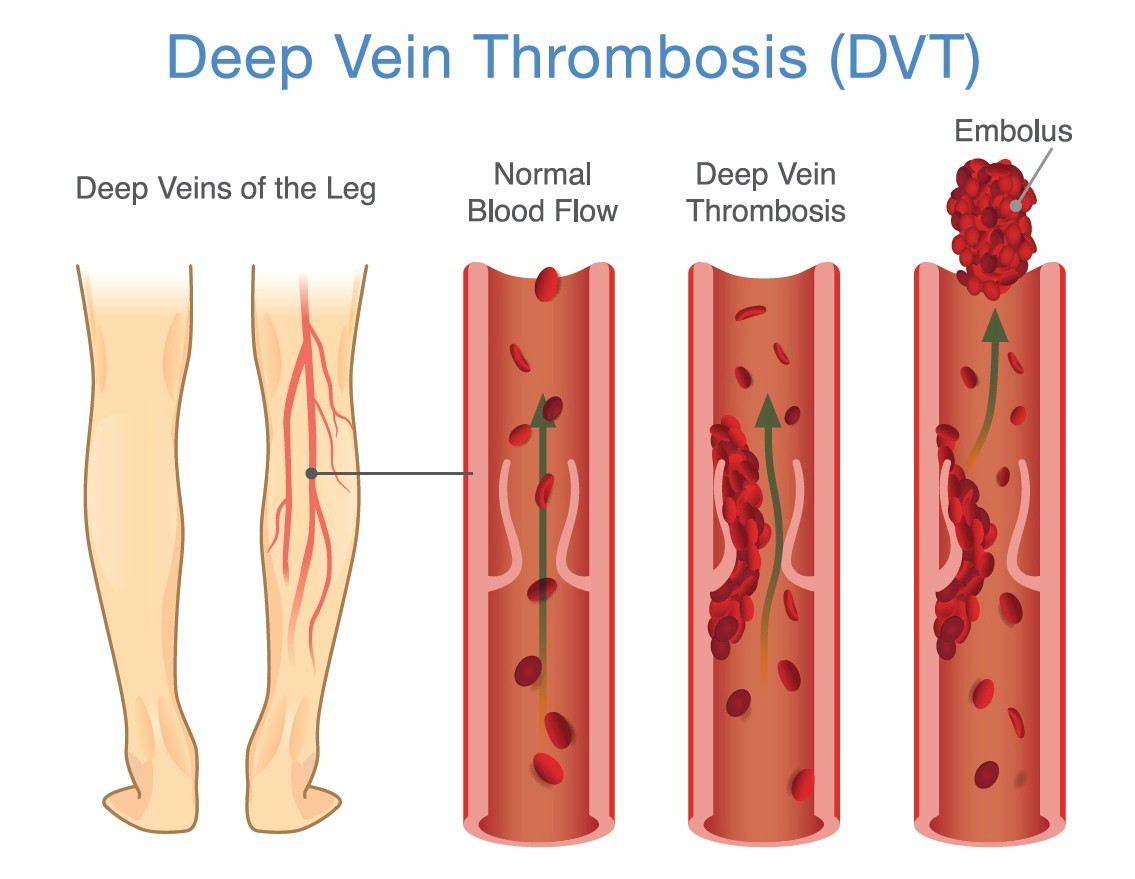
DVT “Deep Vein Thrombosis”
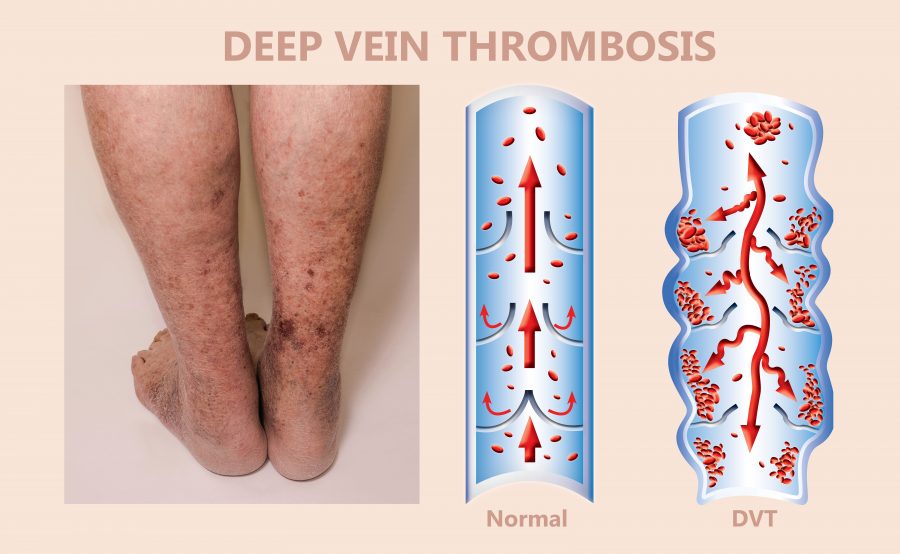
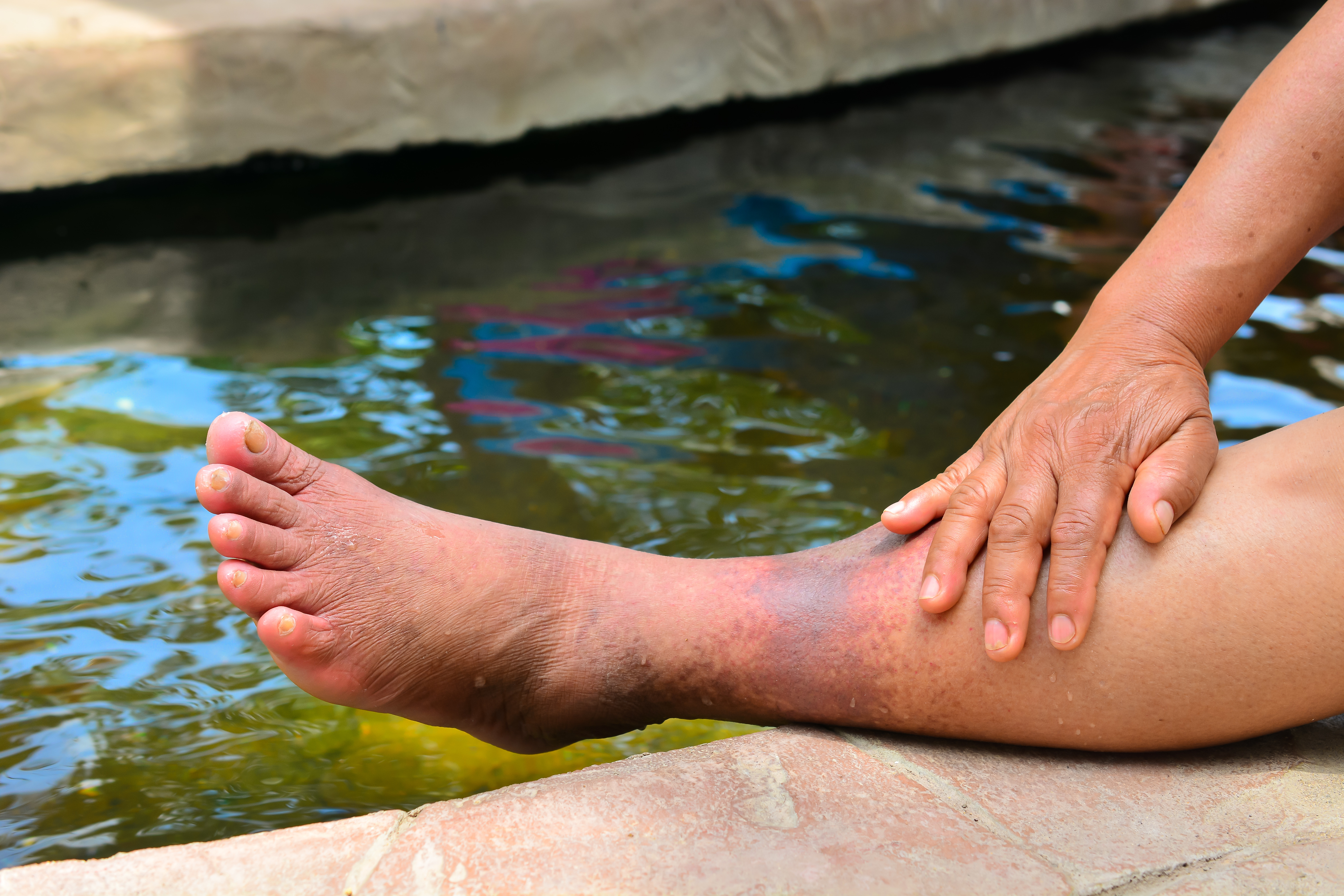
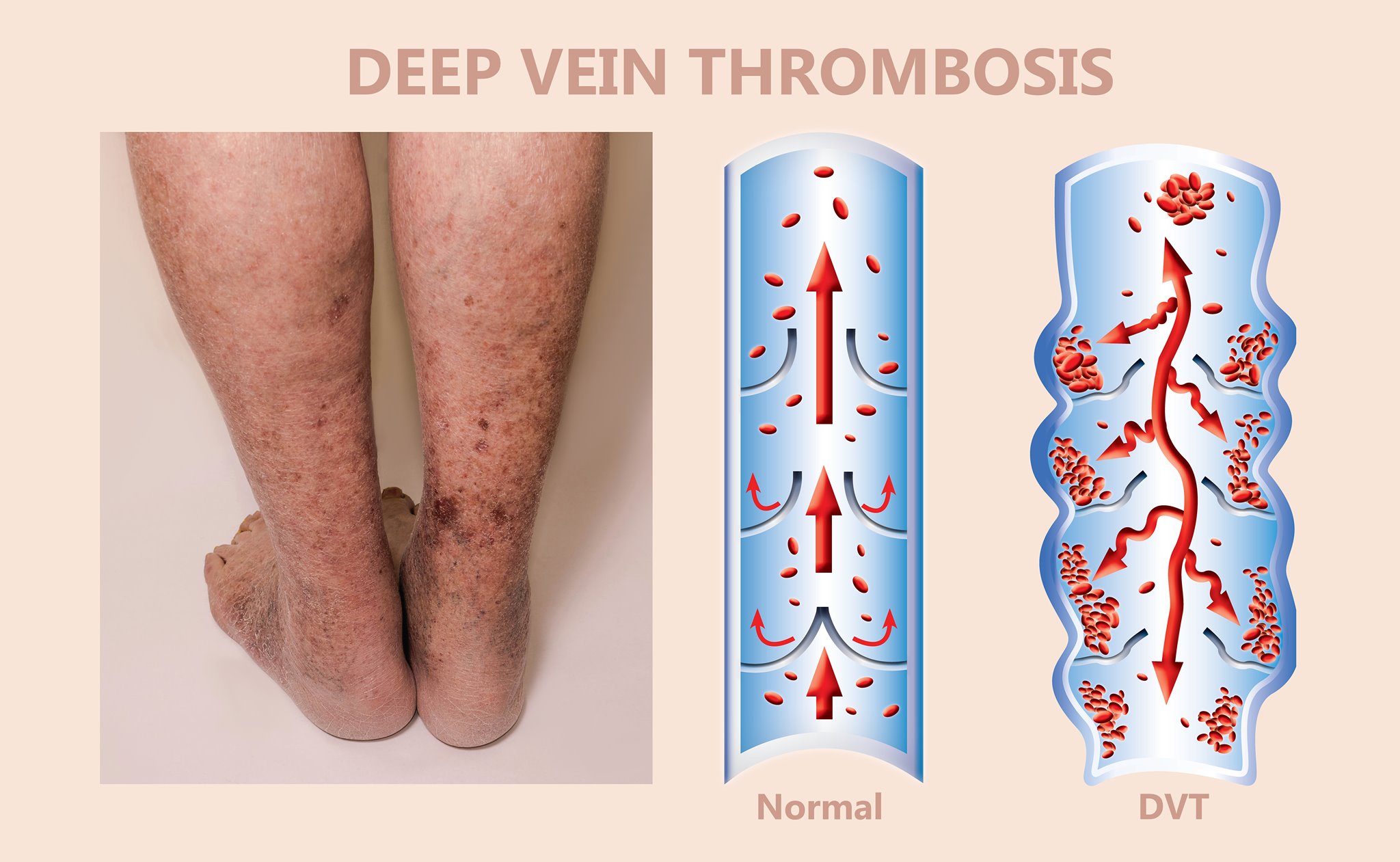
- Most common symptom: new onset leg pain or leg swelling in one leg.
- Leg may turn more red or purple than the other leg.
- A blood clot in a deep vein.
- Deep veins are inside the muscle layer and run alongside the arteries.
- You can’t see a DVT and cannot feel it with your hands.
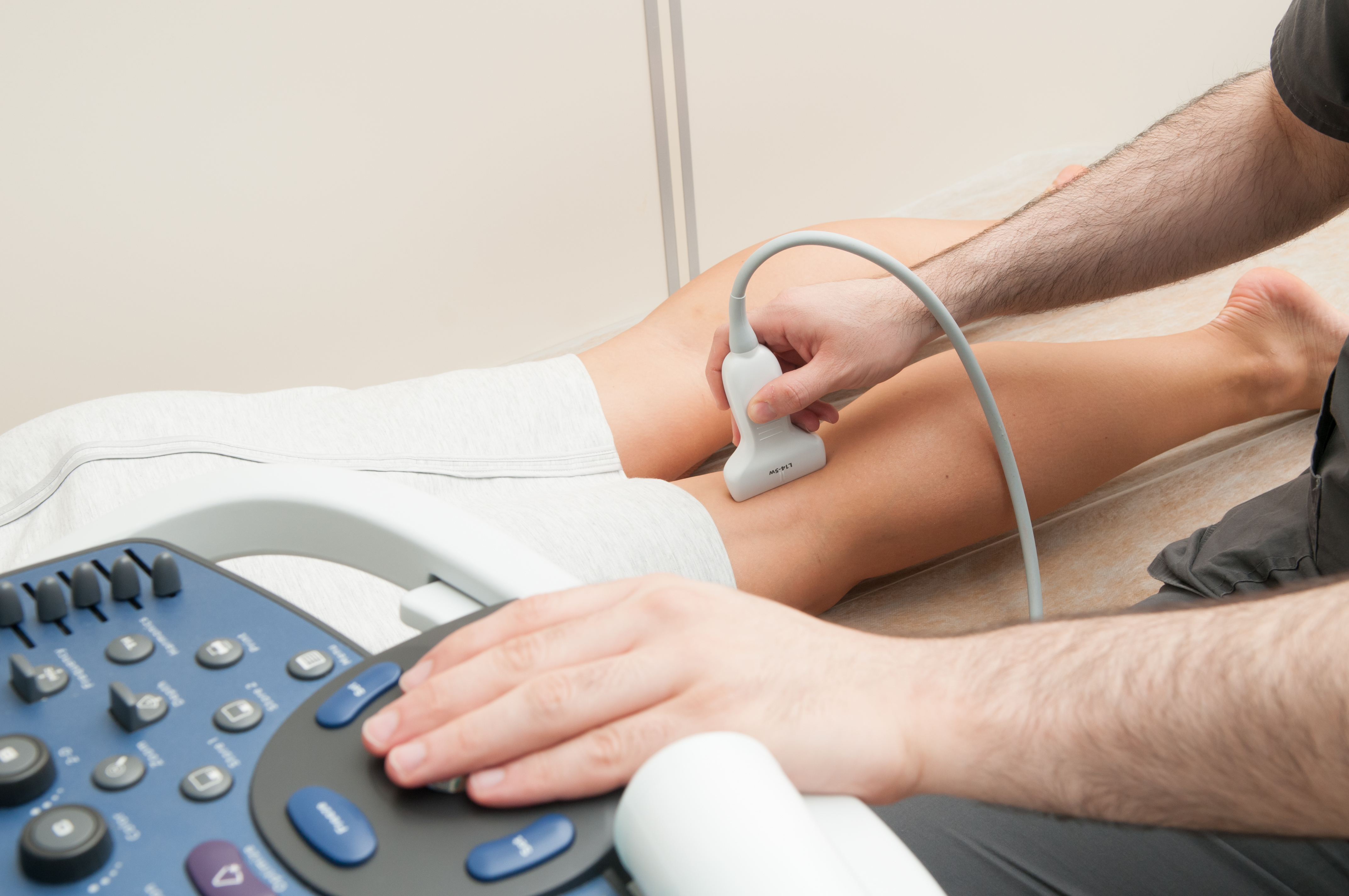
- Doctors have high index of suspicion…If there is any doubt as to the cause of leg pain or swelling, an ultrasound is likely to be ordered.
3 Things Cause Blood To Clot
(VIRCHOW’S TRIAD)
Stasis – This is medical speak for slow blood flow.
- Sudden inactivity-long car ride, long plane trip, prolonged bedrest
- Restriction of blood flow in a vein from internal or external obstruction.
Injury
- Directly to the inner vein inning, getting hit or kicked
- to the body in general, ‘the body’s clotting mechanism gets geared up”.
Hypercoagulability – Conditions that chemically make the blood clot easier than normal.
- Inherited problems: Factor V Leiden, Protein C deficiency, Protein S deficiency, Antithrombin III deficiency, Prothrombin Gene mutation.
- Acquired factors: dehydration (less fluid in the blood), long periods of inactivity (hospitalization, surgery, long trips), polycythemia (body making too many red blood cells), thrombocythemia (too many platelets), and cancer. Antiphospholipid antibody.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Diagnosis
- Leg ultrasound is the standard of care
- CT scans are also effective especially for looking at pelvic veins and for clots in the lungs
- Venogram non filling area when dye is put into vein used infrequently for legs, more often used for pelvic veins.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Treatment
Anticoagulation
- Slows or stops bloods ability to make clot.
- Keeps clot from growing.
- Does not dissolve clot.
- IV Heparin – used in patients in hospital who may need its effect stopped quickly.
- Lovenox – subcutaneous injection once or twice daily.
- Coumadin – oral medication.
- Blocks effects of vitamin K.
- Affected by amt of Vit K in diet.
- Hard to regulate proper dosage.
- Blood work required to adjust dosage.
- Once therapeutic, takes three days to wear off.
- Reverse by Vitamin K or replacement of affected blood components.
- Blood more prone to clotting than normal until proper therapeutic dose achieved.
- Heparin or Lovenox also required while starting and stopping it (Bridging).
- NOACs—New Oral Anticoagulants.
- Don’t require blood monitoring.
- Don’t require bridging.
- Not affected by diet.
- Short acting don’t need reversal agent.
- Xarelto, Eliquis.
Thrombolysis
- Dissolves acute clot, < 2-3 weeks old.
- Tissue Plasminogen Activator (TPA) Alteplase™.
- Systemic– drug goes into arm vein and throughout whole body. Higher risk of bleeding.
- Catheter Directed—drug goes into multi side hole catheter placed directly into clot.
- PharmacoMechanical—drug and mechanical energy used simultaneously to disrupt and evacuate clot.
- Mechanical—open surgical removal of clot.
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
- An implanted device that traps blood clots before they can get to the heart.
- Used when anticoagulation can’t be used.
- Or patient unable to withstand any further heart or lung dysfunction.
- Ideally should be removed after no longer needed.
- Dissolvable filters are being tested.
What Happens After Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
No complications — A doctor orders an ultrasound that shows a blood clot. A blood thinner is given for 3-6 months, the symptoms go away, and that’s the end of it for a majority of patients.
The most common complication of a DVT is “PTS” (Post Thrombotic Syndrome):
- This happens in 20-30% of people that have had a DVT.
- Usually occurs Within a few years.
- Chronic swelling , pain, and discoloration of the leg.
- Results in non-healing venous leg ulcers in 5-10%.
- Compression garments after DVT may reduce PTS occurrence by 50%.
- Most doctors that treat DVT who are not vein specialists.
- Don’t follow patients for PTS.
- Don’t prescribe compression.
- Don’t recognize PTS as a result of DVT.
- Don’t refer patients to a Vein Specialist.
- Don’t recognize leg ulcers are part of the same process.
Most Feared, LEAST common complication of DVT:
- PE (pulmonary embolism).
- Blood clot travels from a vein through the right side of the heart and out into the lungs.
- May be totally silent if small.
- May cause shortness of breath, chest pain or both. Chest pain that is worse with breathing is more likely from PE than MI.
- May cause coughing up blood.
- Death usually not from loss of lung function, but from overload of the right side of the heart.
- If caught in time the clot can be dissolved or removed.
- May be suddenly fatal.
- When this happens many times the patient and doctor never knew there was a clot present. Doctors and hospitals go to great lengths to try to prevent this from happening to patients. They also order lots of tests, mostly leg ultrasounds and CAT scans of the lungs, to try to find them.
From The Blog
March is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Awareness Month
The most dangerous result of a DVT is a Pulmonary Embolism (PE). This is when the Blood clot in the deep vein of the leg breaks loose and goes to the lungs. The most common complication is Post Thrombotic Syndrome (PTS), the gradual development of pain, swelling and...
Let our RVT’s LOOK FOR DVT’s!
Why Vein Specialists of the Carolinas?: • Decreased wait times • Quick results • Each sonographer is a Registered RVT • Will file insurance • Continued aftercare if requested • Dr. Draughn, MD. FACS, RVT, RPVI, RPhS, DABVLM Schedule an appointment today! “All We Do Is...
How Do You Know If You Have Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Most common symptom of DVT is new onset leg pain or leg swelling in one leg. -Leg may turn more red or purple than the other leg. -A blood clot in a deep vein. -Deep veins are inside the muscle layer and run alongside the arteries. -You can’t see a DVT and cannot feel...
CHARLOTTE, NC
Phone
Hours
Mon.-Thurs.: 7:30am - 4:30pm
Friday: 7:30am-12:30pm
Address
15825 Ballantyne Medical Place,
Ste. 240
Charlotte, North Carolina 28277
GASTONIA, NC
Phone
Hours
Mon.-Thurs.: 7:30am - 4:30pm
Friday: 7:30am-12:30pm
Address
860 Summit Crossing Place,
Ste. 120
Gastonia, North Carolina 28054